Argon coagulation
with the use of endoscopic operating modes
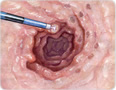 Coagulation of gastrointestinal lesions. In argon coagulation there is no contact of the active electrode with the tissue. Argon coagulation provides penetration depth limited to approximately 3 mm, so it minimizes risk of perforation.
Coagulation of gastrointestinal lesions. In argon coagulation there is no contact of the active electrode with the tissue. Argon coagulation provides penetration depth limited to approximately 3 mm, so it minimizes risk of perforation.
Due to its convenience and safety, Argon coagulation is often used during procedures performed for non oncological indications.
main advantages
- immediate hemostasis helps efficiently coagulate large areas of bleeding surface
- penetration depth limited to approximately 3 mm minimizes risk of perforation
- tissue carbonization is minimal compared to standard electrocoagulation
- no tissue vaporization minimizes the risk of perforation
- no contact between the applicator and tissue means no tissue adhesion
- less surgical smoke gives good visibility of operating area
- reduced smoke eliminates unpleasant odors
- precise application of thermal energy results in reducing procedure time
download
accessories & instruments
Argon electrode connection

MultiSwitch, two-pedal footswitch


Argon flexible probe GIT


top


